1. The angular velocity of the earth around
the sun increases when it comes closer to the sun. Why?
Solution: The angular velocity of the Earth
around the Sun increases when it comes closer to the Sun because of the
conservation of angular momentum. The moment of inertia of the Earth about an
axis measured through the Sun keeps on changing due to changes in its distance
from the Sun. Hence, the angular velocity of the Earth around the Sun
increases because the gravitational pull from the Sun gets stronger.
2.
If the earth were to shrink suddenly what
would happen to the length of the day.
Solution: If the Earth were to
shrink suddenly while keeping its mass constant, the length of a day would
decrease. This is because the length of a day is determined by the Earth’s
rotation on its axis, and the rotational speed of the Earth is determined by
its mass and size. If the Earth were to shrink from its original size, then the
moment of inertia would decrease. By the conservation of angular momentum,
the angular velocity would increase due to its small size and thus the length
of the day would decrease.
3.
What do you mean by moment of inertia?
Solution: The moment of inertia is a measure of
an object’s resistance to changes in its rotational motion. It depends on the
mass of the object and how that mass is distributed relative to the axis of
rotation. The larger the moment of inertia, the more difficult it is to change
the rotational speed of the object.
4.
State the principle of conservation of
angular momentum.
Solution: The principle of conservation of
angular momentum states that the total angular momentum of a closed system
remains constant unless acted upon by external torques. This means that if no
external torques are acting on a system, the angular momentum of the system
will not change.
5.
Can you distinguish between a raw egg and
a hard-boiled egg by spinning each on the table explain.
Solution: Yes, it is possible to distinguish
between a raw egg and a hard-boiled egg by spinning each on a table. The egg
that spins at a slower rate will be raw. This is because in a raw egg, the
liquid matter inside tries to get away from its axis of rotation due to
centrifugal force. This increases the rotational inertia of the egg and it
spins slowly. On the other hand, the hard-boiled egg will have lower
rotational inertia and will spin faster relative to the raw egg.
6.
A ballet dancer stretches her hands when
she wants to come to rest why?
Solution: A ballet dancer stretches her hands
when she wants to come to rest because it is based on the principle of
conservation of angular momentum. When a ballet dancer stretches her arms, the
moment of inertia of the dancer about the axis of rotation increases. Since no
external torque is applied, total angular momentum remains constant. Due
to the increase in moment of inertia, angular velocity decreases and the dancer
comes to rest gradually.
7.
Why it is easier to open the cap of the
pen with two fingers than with one finger?
Solution: It is easier to open the cap of a pen
with two fingers than with one finger because when we use two fingers, two
forces in opposite directions are applied. Rotational motion produced by a
single force is less than two equal and opposite forces. Therefore, it is
easier to open the cap with the help of two fingers rather than one finger.
8.
Will two spheres of equal mass one solid
and other hollow have an equal moment of inertia? Explain.
Solution: No, two spheres of equal mass, one solid and
the other hollow, will not have an equal moment of inertia. The moment of
inertia depends on the mass of the object and how that mass is distributed
relative to the axis of rotation. For a solid sphere, the mass is distributed
closer to the axis of rotation, while for a hollow sphere, the mass is distributed
farther from the axis of rotation. This means that for a given mass and radius,
a hollow sphere will have a larger moment of inertia than a solid sphere.
9.
Explain why spokes are Fitted in the
cycle wheel.
Solution: Spokes are fitted in the cycle wheel
to increase the moment of inertia due to the increase in the distribution of
mass. This opposes the change in the rotary motion of the wheel. Thus,
spokes fitted to the cycle wheel give a steady motion.
10.
A pendulum clock is taken to the moon;
will it gain or loss time. Why?
Solution: A pendulum clock
taken to the moon will lose time. This is because the time period of a pendulum
clock is determined by the acceleration due to gravity. On the moon, the
acceleration due to gravity is lower than on Earth. This means that the
time period of the pendulum will be longer on the moon, and hence, the pendulum
will lose time.
11.
A simple harmonic motion is represented
in usual motion by y=rsin(wt +ϕ),find its acceleration.
Solution: The
acceleration of a simple harmonic motion represented by y = r sin(wt + ϕ) can
be found by taking the second derivative of the displacement with respect to
time. The first derivative gives us the velocity:
v
= dy/dt = r w cos(wt + ϕ)
Taking
the derivative of the velocity with respect to time gives us the acceleration:
a
= dv/dt = -r w2 sin(wt + ϕ)
So,
the acceleration of the simple harmonic motion is a = -r w2 sin(wt +
ϕ).
12.
Define Second's Pendulum.
Solution: A second’s pendulum is a pendulum
whose time period is precisely two seconds; one second for a swing in one
direction and one second for the return swing, for a complete cycle in two
seconds. The length of a simple pendulum that has a period of two seconds is
approximately 0.994 meters.
13.
On what factors does the period of a
simple pendulum depend.
Solution: The period of a
simple pendulum depends on two factors: the length of the pendulum and the
acceleration due to gravity. The period of a simple pendulum is given by the
formula $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\frac{l}{g}} $, where T is the period, L is the length
of the pendulum, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. This means that the
period of a simple pendulum is directly proportional to the square root of its
length and inversely proportional to the square root of the acceleration due to
gravity.
14.
Explain why soldiers are ordered to break
steps while crossing the bridge.
Solution: Soldiers break steps while crossing a bridge to prevent
it from collapsing due to mechanical resonance caused by their rhythmic
marching.
15.
Why do we say that the velocity and
acceleration of a body executing SHM are out phases?
Solution: In simple harmonic motion (SHM),
velocity and acceleration are said to be out of phase because when the velocity
is at its maximum value, the acceleration is zero. This is because acceleration
is the rate of change of velocity. When the magnitude of velocity is maximum,
there will be a stationary point. At that point, the acceleration is zero.
16.
What do you mean by damping? What is its
cause?
Solution: Damping is an influence within or
upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its
oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that
dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. For example, friction can
cause damping by converting mechanical energy of motion into heat.
17.
At what temperature the surface tension
of a liquid is zero?
Solution: The surface tension of a liquid
becomes zero at its critical temperature. At this temperature, there is no
separation of surfaces between the vapor phase and the liquid phase.
18.
Why do clouds seem to be floating in the
sky.
Solution: Clouds seem to be floating in the sky because they are
composed primarily of small water droplets and, if it is cold enough, ice
crystals. The water and ice particles in the clouds are simply too small to
feel the effects of gravity. As a result, clouds appear to float on air.
19.
Why is the bottom of a ship made heavy
explain?
Solution: The bottom of a ship
is made heavy for two reasons. One is to keep the center of gravity of the ship
below the center of buoyancy, which helps to keep the ship in a stable
equilibrium position. The other reason is to increase the moment of
inertia of the ship, which opposes changes in its rotational motion and helps
to keep it steady.
20.
The purity of the gold can be tested by
weighing it in year in water, how?
Solution: You can test the purity of gold by measuring its density
using water displacement. Measure the mass of the gold and the water level in a
graduated cylinder before and after submerging the gold. Calculate the
difference in water levels and divide the mass of the gold by this volume to
get its density. Compare this to the density of pure gold (19.3 g/cc) to
determine its purity.
21.
Why is it easier to lift a body in a
liquid than in air?
Solution: It is easier to lift a body in
a liquid than in air because the liquid provides a greater amount of upthrust
than air does. This is because the density of a liquid is greater than that of
air. The upthrust acting on the body reduces its apparent weight, making
it easier to lift.
22.
Define Surface tension.
Solution: Surface tension is a property of liquids that arises from
the cohesive forces between their molecules. It is defined as the force acting
per unit length on the surface of a liquid, which tends to minimize its surface
area.
23.
Why does hot soup taste better than cold
soup.
Solution: Hot soup is often considered to
taste better than cold soup because the surface tension of hot soup is lower
than that of cold soup. This allows it to spread over a larger area of the
tongue, allowing more taste receptors to be activated.
24.
Explain why liquid drops are spherical in
shape? Explain.
Solution: Liquid drops are spherical in
shape because of surface tension. The inward forces on the surface molecules of
a liquid drop tend to cause the surface to volume ratio as small as
possible. Since surface to volume ratio is minimum for the spherical
shape, a liquid drop is spherical.
25.
What factors does the surface tension of
a liquid depend on, explain.
Solution: Surface tension is caused by
the effects of intermolecular forces at the interface. Surface tension depends
on the nature of the liquid, the surrounding environment and temperature.
Liquids where molecules have large attractive intermolecular force will have a
large surface tension.
26.
Antiseptic used in cuts and wounds of
human flesh have low surface tension, why?
Solution: It should have low surface
tension because liquids with low surface tension can spread easily. So,
antiseptic with low surface tension can spread over cuts and wounds easily and
help to recover faster.
27.
State stokes law.
Solution: Stokes
Law states that the force that retards a sphere moving through a viscous fluid
is directly proportional to the velocity and the radius of the sphere, and the
viscosity of the fluid.
28.
State Bernoulli's theorem.
Solution: Bernoulli’s theorem, also known as Bernoulli’s principle, states that the
total mechanical energy of a moving fluid, which includes gravitational
potential energy of elevation, fluid pressure energy, and kinetic energy of
fluid motion, remains constant.
29.
Small air bubbles rise slowly while big
bubbles rise rapidly through the liquid. why?
Solution: The terminal velocity of bubbles is approximated by Stokes
Law (assuming a spherical bubble). The terminal velocity is proportional
to the square of the radius as well as the density difference between the
bubble and the fluid. A bubble twice as big as another will rise 4 times
as fast. So,
small air bubbles rise slowly while big bubbles rise rapidly through the liquid
because of their terminal velocity.
30.
Define viscosity. Does it depend on
temperature?
Solution: Viscosity is the measure of a
fluid’s resistance to flow. It denotes opposition to flow and can be
thought of as internal friction between the molecules of a fluid. Yes, viscosity does depend on temperature. In
liquids, it usually decreases with increasing temperature, whereas in most
gases, viscosity increases with increasing temperature.
31.
During certain windstorms, light roofs
are blown off. Why?
Solution: During windstorms, light roofs
can be blown off due to differences in air pressure. The air pressure inside a
house is lower than outside. When wind enters a house from an open doorway or
broken window, the air pressure inside will increase and push upwards towards
the roof. Combine this with a suction pulling from on top of the roof and you
have a push-and-pull scenario that increases the likelihood of the roof getting
blown off from the house.
32.
Define Reynold's number?
Solution:
Reynold's number is defined as the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces
within a fluid that is subjected to relative internal movement due to different
fluid velocities.
33.
When a smooth flowing stream of water
comes out of a faucet, it narrows as it falls. Explain.
Solution: When a smooth flowing stream of
water comes out of a faucet, it narrows as it falls due to gravity. Like all
objects, a stream of water also accelerates as it falls. Since the density
of water is constant and water tends to hold together (cohesion), the only
thing that can happen is the narrowing of the stream – which is exactly what
happens.
34.
Why does the temperature of a gas undergo
adiabatic expansion decrease?
Solution: In an adiabatic expansion, a gas does work at the cost of
its kinetic energy and so its random motion is reduced. According to the
kinetic theory, the temperature of a gas is associated with its random
motion. This is why the temperature of a gas drops in an adiabatic
expansion.
35.
Why does a gas have two specific heat
capacities?
Solution: A gas has two specific heat
capacities because the measurement of specific heat for gases can be affected
by many state variables of the system such as temperature, pressure, and
volume. Therefore, we use two methods to measure the specific heat of gases,
which are at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp).
36.
Is Cp always greater than
Cv?
Solution: Yes, Cp is always greater than Cv for
gases. When a gas is heated at constant pressure, expansion in the volume with
an increase in the internal energy of the system takes place. Hence, Cp is
greater than Cv.
37.
What are the limitations of the first law
of thermodynamics.
Solution: The first law of thermodynamics has several
limitations.
·
It does not state anything about the heat flow direction.
·
It does not indicate whether heat can flow from a cold body to a hot
body.
·
The first law also does not tell anything about the condition under which
heat can be converted into mechanical work.
38.
Why does a refrigerator consume more
power in summer than in winter to cool the same quantity of food by the same
degree?
Solution: A refrigerator consumes more power in summer than in winter to cool the
same quantity of food by the same degree because heat pumps are designed to
move thermal energy opposite to the direction of spontaneous heat flow by
absorbing heat from a cold space and releasing it to a warmer one. Due to
surrounding temperature, a refrigerator consumes more power in summer than in
winter to cool the same quantity of food by the same degree.
39.
Can a room be cooled leaving the doors of
electric refrigerator open in a closed room? Explain.
Solution: No, a room cannot be cooled by
leaving the doors of an electric refrigerator open in a closed room. In
fact, the temperature of the room will rise because the refrigerator extracts
heat from its freezing chambers and rejects it to the surrounding air in the
room.
40.
Explain the significance of the second
law of thermodynamics.
Solution: The second law of thermodynamics is significant because it
explains why certain processes occur and others do not. It states that as
energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The
second law also states that there is a natural tendency of any isolated system
to degenerate into a more disordered state.
41.
Petrol engines are less effective than
diesel engines. Explain why?
Solution: Because diesel has a lower ignition temperature than
petrol. Diesel is more combustible than petrol, therefore less fuel is required
to generate the same amount of power. Secondly, petrol doesn't undergo complete
combustion and hence there is a small wastage of fuel. This is why diesel engines
are more efficient than petrol engines.
42.
Explain why the temperature of the gas
drops in the adiabatic process?
Solution: During
adiabatic expansion, the gas is allowed to expand quickly work is done by the
gas during its expansion. So, its internal energy decreases. As heat can't be
enter the same system for the surroundings, the temperature of gas falls.
43.
State second law of thermodynamics.
Solution: It states that, “It is impossible to get
continuously supply work done from a body by cooling it to a temperature than
that of its surrounding.”
44.
Can longitudinal waves be polarized?
Explain.
Solution: No, because they are the wave in which the vibration of a party called
takes place in the direction of the motion of the waves. Thus, the longitudinal
wave is already polarized in the direction of the motion of the waves.
Therefore, longitudinal waves are not polarized.
45.
Distinguish between progressive waves and
stationery waves.
Solution:
|
Progressive Wave |
Stationary waves |
|
No particle is permanently at rest. |
All the particles of nodes are
permanently at rest. |
|
At every point there is vibration in
pressure. |
Pressure vibration is maximum at nodes
and zero at antinodes. |
|
Energy is transmitted from particle to
particle. |
Energy is not transmitted from
particle to particle. |
46.
Frequency is the most fundamental
property of a wave. Why?
Solution:
Frequency is the only physical quantity that is independent of the
nature of media through which the wave is propagating. When a wave travels
its wavelength as well as velocity may changes but its frequency remains
unchanged. This is the reason for frequency to be a fundamental property.
47.
Which types of waves propagate in the
liquid, Explain.
Solution:
For the propagation of the transverse wave, the modulus rigidity of the
medium is responsible and for the propagation of the longitudinal wave, the
bulk modulus of elasticity is responsible. A sold has both moduli of rigidity
and bulk modulus but liquids only have bulk modulus. Hence only longitudinal waves
can propagate in the liquids.
48.
The speed of sound in humid air is more
than that in dry air, why?
Solution: The velocity off sound is inversely
proportional to the square root of its density.
The density of water vapor is smaller than that of dry air, and the
presence of moisture un air reduces the density of air in atmosphere. So, Velocity
of Sound is more in moist (humid) air than dry air.
49.
Define an organ pipe.
Solution:
The hollow wood or metallic tube which is used to produce musical sound
is called organ pipe.
50.
When we start filling an empty bucket
with water, the pitch of sound produced goes on changing. Why?
Solution:
a bucket can be treated as pipe closed at one end. The frequency of the
note produced =v/4l, where v is velocity of sound and l is length of air
column, which is equal to depth of water level from the open end. As a bucket
is filled with water length (l) decreases. Therefore, frequency of sound
produces goes on increasing.
51.
Bells are made of metal but not wood.
Why?
Solution:
Bells are made from metals because metals have the capability to produce
sound when hit with a solid object, i.e, they are sonorous. Wood is not
sonorous, and is a non-metal.
52.
Why is sounding board used in a string
instrument?
Solution: the stringed instrument is provided
with a hollow box called a soundboard. When the strings are shaped into
vibrations forced vibration are produced in the sound board. Since the
soundboard has a large area, it sets the large volume of air into vibration.
This produces a loud sound of the same frequency as that of the string.
53.
When the tension in a given stretched
string is increased by four times, by what factor does the velocity of
transverse wave in the string change?
Solution:
54.
What do you mean by resonance?
Solution: A
phenomenon in which an external force or a vibrating system forces another
system around it to vibrate with greater amplitude at a specified frequency of
operation.
55.
Why is an end correction necessary for an
organ pipe?
Solution: Rayleigh find out that when an air in
a organ pipe vibrates, the reflection of the sound waves takes place a little
above the rim of the organ pipe. Due to this reason, the vibrating length of
the air column is greater than the actual length of the organ pipe. Therefore,
in order to get accurate value for frequency of vibration, the end correction
is taken into account.
56.
State Doppler's effect.
Solution: The apparent change in frequency of a
wave when there is relative motion between source and observer is called
Doppler effects.
57.
How is it that one can recognize a friend
from his voice without seeing him?
Solution: Through the quality of the sound one
can recognize his friends from his voice with out seeing him. The quality of
sound released from the vocal of person is different for everyone because the
overtone is different for different person. The quality of sound helps to
distinguish between two sounds. The overtones present in different voices are
different even at same frequency. In this way one can recognize his friend from
voice.
58.
Justify the proverb "An empty vessel
makes much noise".
Solution: The air molecules in empty vessel
vibrates with greater amplitude and greater intensity than liquid molecules
filled vessel.
59.
Why are longitudinal waves called
pressure waves.
Solution: The propagation of the longitudinal
waves in medium involves change in pressure and volume of the air during
compression and rarefaction formation. So, longitudinal waves are called as
pressure waves.
60.
Define beats and beat frequency.
Solution:
The beat frequency is equal to the complete value of the alteration in
the frequency of the two waves. The count of beats per second is equivalent to
the difference in frequencies of two waves is called beat frequency.
61.
Differentiate between a plane wave front
and a spherical wave front.
Solution:
|
Plane wave front |
Spherical wave front |
|
As the spherical or cylindrical wave
front advances, its curvature decreases progressively. so a small portion of
such wave front at a large distance from a point source or linear source will
appear a plane and hence termed as plane wave front. |
It is produced by the point source of
light. This is because all such point which are equidistance from the point
source lie on sphere. |
62.
What is meant by wave front and wavelets?
Solution: Wave front is the locus of all
adjacent points which are equidistance from the source of light and are
vibrating in same phase. Every point on the wave front acts as a source of
disturbance, these disturbance from the points are called wavelets.
63.
What is Huygens's principle?
Solution: Huygens’s
principle is based on following assumptions:
Each point on a wave front act as a new source of
disturbance. The disturbance from these points is called secondary wavelets.
These wavelets spread out in all direction in medium with the velocity of
light.
The new wave front is tangent plane or tangent
envelope to all secondary wavelets from the secondary source.
64.
The width of fringes obtained in a double
slit experiment is 4mm. If one slit is closed, what will happen to the
interference fringes?
Solution: When one slits is completely closed
then diffraction pattern will be observed instead of interference pattern.
65.
What happens on the interference fringes
in a young's double slit experiment when
i) the screen is moved away.
ii) the source is replaced by another source of
shorter wavelength.
Solution:
i) When the screen is moved away from the double-slit,
the fringes become wider and farther apart.
ii) If the source is replaced by another source of
shorter wavelengths, then the fringe, width decreases, and interference bands
are not seen directly.
66.
What are the conditions for destructive
and constructive interference of light waves.
Solution:
For constructive interference, the path difference
between two interfering waves should be an integral multiple of the wavelength.
For destructive interference, the path difference
between interfering waves should be half of odd number integral multiple of
wavelength.
67.
Distinguish between interference and
diffraction.
Solution:
|
Interference |
Diffraction |
|
Interference
is the phenomenon of two or more waves overlapping and producing a resultant
wave with a higher or lower amplitude depending on their phase relationship. |
Diffraction
is the bending of waves around an obstacle or through an aperture, resulting
in the spreading out of the wavefront. |
|
It is caused
by the superposition of waves from two or more coherent sources. |
It is caused
by the interaction of waves with an obstacle or aperture. |
|
It results in
the formation of interference fringes or bands of bright and dark regions. |
It results in
the formation of a diffraction pattern or series of alternating bright and
dark regions. |
68.
What is the diffraction of light?
Solution: the phenomenon of bending of the
light around the corner and spreading around the region of a geometrical shadow
is called diffraction of light.
69.
Does polarizing angle depend on
wavelength of light.
Solution: the angle of incident is known as polarizing angle for which the reflected ray is completely polarized. The refractive index of a transparent medium depends upon the wavelength by the Cauchy relations:
\[\mu = A + \frac{B}{{{\lambda ^2}}} + \frac{C}{{{\lambda ^4}}}\]
Again, we know the polarizing angle θp =
tan-1µ from these two relations it can be said polarizing angle
depend upon the wavelength of the light.
70.
Can sound waves be polarized? Justify
your answer.
Solution: No, sound wave cannot be polarized.
It is because sound waves are longitudinal waves. (q.no. 44)
71.
Differentiate unpolarized and polarized
light.
Solution:
|
Unpolarized |
Polarized |
|
The light having vibration of the
electric field vector in all direction in a plane perpendicular to the
direction of propagation of the light is known as unpolarized light. |
The light having vibration of electric
field vector along single straight line perpendicular to the direction of
propagation of the light is known as polarized light. |
|
Changing intensity of emergent light
is observed when polarized light passed through a single rotating crystal. |
There is no change in intensity of the
emergent light, when unpolarized light passed through a single rotating
crystal. |
72.
What is the principle of potentiometer?
Solution:
The principal of
the potentiometer is that for a wire having uniform area of cross
section and uniform composition, the potential drop is directly proportional to
the length of wire.
73.
Is polarization possible in longitudinal
waves? why?
Solution: No, because they are the wave in
which the vibration of a party called takes place in the direction of the
motion of the waves. Thus, the longitudinal wave is already polarized in the
direction of the motion of the waves. Therefore, longitudinal waves are not
polarized.
74.
State the principle of potentiometer and
write down its one application.
Solution: The principal of
the potentiometer is that for a wire having uniform area of cross
section and uniform composition, the potential drop is directly proportional to
the length of wire.
Application: Potentiometer is used to measure
the potential difference between two points.
75.
Why do we prefer a potentiometer with
longer wire.
Solution: With the increase in length
potentiometer becomes more sensitive. The fall of potential is proportional to
the length of the wire only if the wire is of a uniform thickness.
76.
Why do we prefer a potentiometer to
measure the emf of a cell rather than a voltmeter?
Solution: The potentiometer measures the
potential difference with less error as compared to voltmeter. If the
potentiometer is used, it doesn’t draw any current from the cell and hence
gives the actual value of the EMF of the cell whereas when a voltmeter is used
to measure the EMF of the shell, it draws some current from the cell and hence
it gives a reading less than the actual value of the EMF of the cell.
77.
A voltmeter has high resistance, explain,
why?
Solution: A voltmeter measures the
voltage difference between the two different points, but it should not change
the amount of current going through the element between these two points. So,
it should have very high resistance so mat it doesn't draw current through it
78.
State and explain Kirchhoff's law of
electric circuits.
Solution: Two Kirchhoff’s laws are:
(i) First Law: It states that the
algebraic sum of the current at a junction of an electric circuit is zero.
(ii) Second Law: It states that in a
closed loop the electric circuit, algebraic sum of the emfs is equal to the
algebraic sum of the potential difference in the various part of the loop.
79.
The resistance of an ammeter must
essentially be very small, why?
Solution:
An ammeter is a low resistance galvanometer. When it is connected in series in
a circuit, the resistance of the circuit does not increase appreciably and
consequently but if the resistance of the ammeter is high, the net resistance
of the circuit becomes very high and the current in the circuit reduces and
hence ammeter is not able to measure accurate current. Due to this reason, the
resistance of an ammeter must be essentially be small.
80.
What is thermoelectric effect?
Solution:
the phenomenon in which electrical energy is produced from the thermal energy
is known as thermoelectric effect.
81.
Does the thermoelectric effect obey the
law of conservation of energy? Justify.
Solution:
Yes, thermoelectric effect obeys the law of conservation of energy. In the
Seebeck effect we see heat energy is converted into electrical energy whereas
in the Thomson effect electrical energy is converted into heat energy and in
the Peltier effect one junction absorbed the heat while another junction
evolves or releases the heat. Hence, we can say that thermoelectric effect
obeys the law of conservation of energy
82.
What is the temperature of inversion? On
what factors does it depend.
Solution:
the temperature of the hot junction at which thermal EMF is zero and changes
its polarity beyond it is known as temperature of inversion. Temperature of
inversion depends on the temperature of the cold junction and also the type of
the thermocouple used.
83.
What is neutral temperature? On what factors
does it depend?
Solution:
the temperature of the hot junction at which Thermo-EMF becomes maximum and
neutral temperature is constant for a given thermocouple.
84.
What is thermopile?
Solution:
Thermopile is the device which is used to detect or measure the amount of heat
radiation.
85.
What is the better representation of the
Lorentz force?
Solution: The
Lorentz magnetic force is given by the following relation:
$\overrightarrow F $=q ($\overrightarrow V $ × $\overrightarrow B $)
Here q is the magnitude of the moving charge.
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane containing
the velocity vector $\overrightarrow V $ and the magnetic field
vector $\overrightarrow B $.
86.
State Fleming Left hand rule.
Solution:
Fleming's left-hand rule can be stated as stretching the forefinger, middle
finger, and thumb of the right hand such that they are mutually perpendicular
to each other.
87.
Why are the pole pieces of magnets cut
into cylindrical form in a galvanometer.
Solution: The major purpose of making pole
pieces of magnets into cylindrical form is to ensure that the magnetic
field produced in the moving coil galvanometer is strong and also radial
88.
What do you mean by hall effect? Why is
it more effective in semiconductors.
Solution: When a magnetic field is applied to a current
carrying conductor, a voltage is developed across the specimen in the direction
perpendicular to both the current and the magnetic field. This effect is known
as halls effect.
The
density of charge carriers is less in semiconductors. Since Hall voltage is
inversely proportional to the number of charge carriers, it is more effective
in the case of semiconductors.
89.
Define one ampere in terms of the force
between current carrying conductors.
Solution: One ampere is that current following in each of two
infinitely long parallel conductors 1 meter apart such that the force permitter
length on each conductor is 2×10-7N.
90.
State ampere's theorem.
Solution: Ampere's Circuital law states that, “the line integral of the magnetic field around any closed path in free space is equal to µ0 times the total current enclosed by the path.
\[\oint {\mathop B\limits^ \to } .d\mathop l\limits^ \to = {\mu _0}I\]
91.
What is Curie temperature?
Solution:
The temperature at which a ferromagnetic substance loses its ferromagnetism and
attains Para magnetism is known as Curie Temperature.
92.
Distinguish between diamagnetic and
paramagnetic substances in terms of their relative permeability and
susceptibility.
Solution:
|
Diamagnetic |
Paramagnetic substances |
|
Its relative permeability is less than
1, usually 0.9999. |
Its relative permeability is more than
1. |
|
Magnetic Susceptibility is small and negative. |
Magnetic Susceptibility is small and
positive. |
93.
What is the significance of the area of a
hysteresis loop.
Solution: The area of the hysteresis loop measures the amount
of energy that is basically lost per cycle of magnetization. The area of
the hysteresis curve for steel is more than that of soft iron. The magnetic
materials whose B-H curve is more are useful for making permanent magnets.
94.
Permanent magnets are made of steel, why?
Solution:
Steel is used for making permanent magnet because its magnetism does not
destroy easily by external magnetic field.
95.
What is retentivity and coercivity of a
ferromagnetic material?
Solution: The tendency of the
magnetic material to maintain magnetism, even in the absence of a magnetizing
field, is known as retentivity.
Coercivity in a ferromagnetic material
is the intensity of the applied magnetic field (H field) required to
demagnetize that material, after the magnetization of the sample has
been driven to saturation by a strong field.
Note: Ferromagnetic materials have
high permeability and low retentivity.
96.
Above Curie temperature a ferromagnetic
material became para magnetic, why?
Solution: A ferromagnetic material follows
Curie law and the alignment of the atomic magnetic moments in it is disturbed
with increase of the temperature. Above the Curie temperature this alignment is
completely random due to thermal motion of the atom and the material becomes
paramagnetic.
97.
Define Eddy Current.
Solution: the induced circulating current produced in
a metal itself due to change in magnetic flux linked with the metal is known as
Eddy current.
98.
Define magnetic flux.
Solution: The number of magnetic lines of force
crossing through the surface is known as magnetic flux.
99.
State Faraday's law of electromagnetic
induction.
Solution: Friday’s law of electromagnetic
induction states that
When the magnetic flux linking a conductor are equal
changes an EMF is induced in it.
The induced EMF lasts as long as the change in
magnetic flux continues.
The magnitude of induced EMF in a conductor or a coil
is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage.
100.
A bar magnet falls through copper ring.
Will its acceleration be equal to g? Justify.
Solution: When the bar magnet approaches the
ring, the magnetic flux linked with the ring increases so an EMF is induced in
the ring. If the ring forms a complete conducting loop, the current is also
induced. According to the Lenz law, the current opposes the approach of a
magnet and hence the acceleration of a magnet becomes less than the value of
acceleration due to gravity.
101.
Bird sitting on a high-tension line wire
flying up when current is switched on, why?
Solution: As
soon as the current is switched on in a high voltage
wire the bird sitting on it flies away. The reason
being due to induced current flowing throughout the body of
the bird, which flows in the opposite direction through the wings of
the birds. Hence, the wings experience a force of mutual repulsion.
102.
Lenz law closes the principle of
conservation of energy. Explain.
Solution: Yes, Lenz's law follows the principle
of conservation of energy. The law of conservation of energy states that energy
can neither be created nor be destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to
another. Lenz's law states that the direction of current is such that it
opposes the change in the magnetic flux. So, an extra effort is required to do
work against the opposing force. This extra effort is converted into electrical
energy, which can be viewed as the law of conservation of energy.
103.
Does Lenz Law violate principle of
conservation of energy, explain.
Solution: No, Lenz law do not violate the law
of conservation of energy. In fact, Lenz's law follows the principle of
conservation of energy. The law of conservation of energy states that energy
can neither be created nor be destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to
another. Lenz's law states that the direction of current is such that it
opposes the change in the magnetic flux. So, an extra effort is required to do
work against the opposing force. This extra effort is converted into electrical
energy, which can be viewed as the law of conservation of energy.
104.
220-volt AC is more danger than 220-volt
DC, why?
Solution: 220-volt a.c. means the effective or
virtual value of a.c. is 220 volts, i.e., Ev=220 volt. But 220-volt d.c. has
the same peak value (i.e., 220 volts only). Moreover, the shock of a.c. is
attractive and that of d.c. is repulsive. Hence 220-volt a.c. is more dangerous
than 220 volts d.c.
105.
Why is choke coil preferred over
resistance in AC?
Solution: Choke coil is preferred over resistor in ac circuit
because the phase difference between current and voltage is Φ=90˚ due to which
power loss becomes zero.
i.e., P = EvIvCosΦ = EvIvCos90=0
Since choke coil acts as inductor and has large value
of self-inductance making power dissipation zero(nearly).
106.
Define rms values of alternating current.
Solution: RMS value of AC current is that
steady current which when passed through a resistance for a given time produces
the same amount of heat as the alternating current does in the same resistance
in the same time.
107.
Define quality factor of resonance in a
series LCR circuit.
Solution: the quality factor of the resonance
in the series LCR circuit is defined as the sharpness of a tuning of a
resonance. The quality factor of series resonant circuit is defined as the ratio
of the voltage developed across the inductance or capacitance at resonance to
the impressed voltage, which is the voltage across the resistance.
108.
Explain why two parallel wires carrying
current in the opposite direction repel each other?
Solution:
When two free parallel wires carry currents in opposite direction, the
two magnetic fields created by it will also be opposite to each other, so they
will repel.
109.
Can a uniform magnetic field be used to
speed up a charged particle? Explain.
Solution: The magnetic field accelerates
the charged particle by changing the direction of velocity. The magnetic field
doesn't change the speed of the charged particle.
The reason is that the magnetic field doesn’t affect
the speed is because the magnetic field applies a force perpendicular to the
velocity. Hence, the force can’t do work on the particle. As a result, the
particle can’t change its kinetic energy. So it cannot change the speed.
110.
Can a holes be created in a metal?
Justify your answer.
Solution:
In a conductor, the forbidden band is missing and the conduction band
and valance band are overlapped. Therefore, no holes can be created in a
metal.
111.
At high frequencies, a capacitor becomes
a short circuit, and an inductor becomes an open circuit explain.
Solution:
At high frequencies the capacitive reactance of a capacitor becomes
very small, nearly approaches to zero and capacitor behaves like a wire. So, it
acts as a short circuit.
While in the inductor there is large opposition to
the flow of a.c. at very high frequency and the current cannot flow through
the inductor.
112.
What is meant by watt-less current.
Solution: The current through pure inductor or
pure capacitor which consumes no power for its maintenance in the circuit is
known as ideal current or what less current.
113.
What path does the electron follow in
electric field when the electron is projected normally in the field?
Solution: when an electron is projected
perpendicular to a uniform electric field it experiences an electric force in
opposite direction of the field. Thus, when electron moves perpendicular to the
electric field its trajectory is parabolic in nature.
114.
What property of the cathode rays
indicates that they consist of electrons?
Solution: cathode are the stream of negatively
charged particle which gets deflected by the electric and magnetic field points
means it consists steam of electrons.
115.
Cathode rays cannot be regarded as
electromagnetic waves, why?
Solution: cathode ray are the stream of
negatively charged particle which gets deflected by the electric and the
magnetic field but electromagnetic waves are chargeless particle which are not
deflected by the electric and the magnetic field hinge cathode ray are not the
electromagnetic waves.
116.
Lightning takes place at a higher
altitude than at a lower altitude. Why?
Solution: the electric field set up in the
atmosphere causes lightning discharge if the pressure is low. Therefore, due to
the low pressure at high altitude the electric discharge take place and hence
we found lightning mostly takes place at the higher altitude.
117.
Can photoelectric effect be explained on
the basis of wave theory of light? justify your answer.
Solution: Wave nature of radiation cannot explain the photo
electric effects because of :
(i) The immediate ejection of photo electrons
(ii) The presence of threshold frequency for a metal surface.
(iii) The fact that kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is independent of
the intensity of light and depends upon its frequency.
Thus, the photoelectric effect cannot be explained on the basis of wave nature
of light
118.
What happens to the kinetic energy of
photo electrons when intensity of light is doubled?
Solution: If the energy of a photon is greater
than the work function of the material, the electron may escape from the
metallic surface. Greater the intensity of the light at a particular frequency
means greater the number of the photon’s incident per second and hence the
greater the number of photoelectrons limited for second. Hence, there will be
no effect on the kinetic energy of the photoelectron if the intensity of the
light is doubled
119.
What is meant by stopping potential?
Solution: the minimum retarding potential at
which photoelectric current becomes zero is called stopping potential. It is
denoted as V0.
120.
What is the threshold frequency?
Solution: The minimum frequency of incident
radiation which is just sufficient to eject an electron from the surface of the
metal is known as threshold frequency.
121.
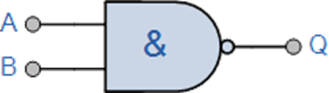
What are logic gates? Give a two-truth
table for a two input NOR gate.
Solution: A logic gate is a digital circuit
which has one or more input and one output. It follows the short and logical
relationship between the input and the output voltage.
|
Symbol |
Truth Table |
||
|
2-input NOR Gate |
B |
A |
Q |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
Boolean Expression Q = A+B |
Read as A OR B gives NOT Q |
||
122.
What is truth table? Write down the truth
table for a two input NAND gate.
Solution: The table giving the different
possible input and the corresponding output of a logic gate is called its truth
table.
|
Symbol |
Truth Table |
||
|
2-input NAND Gate |
B |
A |
Q |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
Boolean Expression Q = A.B |
Read as A AND B gives NOT Q |
||
123.
Why is x-ray radiation process called
inverse photoelectric effect?
Solution: when the fast-moving electron strike
on a high atomic weight substance X-ray is produced and when the radiation of a
sufficient frequency incident on a metal surface electron are emitted that is
photoelectric effect take places. It means fast moving electron produces X-ray
and X-ray i.e., radiation produces photoelectron. Hence X-ray is the reverse
phenomenon of photoelectric effect.
124.
A proton and an electron have the same
de-Broglie wavelength. which one has greater kinetic energy explain
Solution: de-Broglie wavelength in terms of
kinetic energy is represented as $E = \frac{{{h^2}}}{{2m{\lambda ^2}}}$.
Since, λ is same for both particle, E α $\frac{1}{m}$.
As the mass of an electron is less than that of the photon show energy of the
electron is greater than photon.
125.
The wave nature of particle is not
observable in daily life, why?
Solution: From de Broglie equation, λ = $\frac{h}{mv}$,
it is clear that the lighter the particle the greater the de Broglie wavelength
and the faster the particle moves, The smaller is its de Broglie wavelength.
The wave nature of the matter can be apparent if the wavelength of the wave
associated with the moving matter is of the size of the matter. In the daily
life, particles are heavier and they move with comparatively low speed hence
this is not observable in our daily experiences.
126.
What do you mean by matter waves?
Solution: according to the de Broglie the wave
is associated with each moving particle which is known as matter waves. When
the particles are in motion matter wave are produced. The velocity of matter
waves depends upon the velocity of the particle in the motion.
127.
What do you mean by uncertainty
principle?
Solution: Uncertainty principle states that it
is impossible to determine precisely and simultaneously the value of both position
and the momentum in atomic system.
128.
Point out the importance of de-Broglie
wave.
Solution: The importance of the De Broglie wave
are follows:
A matter particle will have a wavelength associated
with it and only if it is in motion. The greater the momentum the shorter will
be the wavelength.
Two different velocities are associated with a
material particle in motion one refer to the mechanical motion of the particle
and other refer to the propagation of the associated wave.
It justifies Bohr’s quantum condition of the hydrogen
atom i.e., the stable state of the electron in the atom are governed by the
integral rule.
Bohr’s postulate of atomic model is:
129.
State Bohr’s postulate of atomic model.
Solution: Bohr’s Postulates of atomic models
are:
Electron revolves around the nucleus on certain
permitted orbits of definite radii.
Electron can revolve around the nucleus in only those
permissible orbits whose angular momentum is integral multiple of h/2π.
130.
If a radioactive nucleus Has a half-life
of one year, will it be completely decayed at the end of two years explain.
Solution: No, it doesn’t mean that a particle
with one year half life gets vanished after two years. On increasing time, the
particle starts to decay, and along with decaying the half-life of undecayed
materials also increases exponentially.
131.
How does a daughter nucleus differ from
its parent when it emits i) an alpha particles ii) gamma rays.
Solution: In alpha decay, the mass of daughter nucleus
mass gets decreased by four units and atomic number decreases by two units.
For gamma decay, there is no change in mass and charge
or there is no difference in parent and daughter nucleus with respect to mass
and charge.
132.
Nucleuses contain no electrons, yet it
ejects them explain.
Solution: When a nucleus disintegrates, it
emits β rays, known as β decay. Β-particles
are nothing but they are electron.
133.
There are no electrons inside the
nucleus, but they are emitted from an unstable nucleus, why?
Solution: A nucleus contains no electron but it can emit The nucleus
ejects anti neutrinos which are kind of electrons. This process is mediated by
the weak interaction. The neutron turns into a proton through the emission of a
virtual W- boson. ... The virtual W- boson then decays into an electron and an anti-neutrino.
134.
How do Beta particles differ from
electrons?
Solution:
Electron and beta particles are essentially same, but the electron ejected by nucleus
is said to be a beta particle.
135.
Higgs boson gives the complete picture of the
universe. Comment on it.
Solution:
136.
What are the uses of radioisotopes?
Solution:
Radioisotopes can be used in various field in today’s world. It can be used to
make medicine for curing various disease, it can be used as the source of
energy and also be used for carbon dating.
137.
What is the meaning of ionization energy
of hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV?
Solution: The ionization potential of hydrogen is 13.6 electron volts
(eV), which means that an electron in a hydrogen atom requires at least 13.6 eV
of energy to be removed from the atom.
138.
What is the difference between an
electron and a β -particle.
Solution:
|
Electron |
β -particle |
|
Electrons are present in the atom
revolving around the nucleus. |
β -particle are originated
from atomic nuclei during beta decay. |
|
It always has -1 charge. |
It may have -1 or +1 charge. |
139.
What are seismic waves?
Solution: The energy that travels under the surface layer of the earth and causes
an earthquake is called seismic waves. They are also called as elastic waves
because they cause deformation of the materials when they propagate.
140.
Differentiate between P-wave and S-wave.
Solution:
|
P-wave |
S-wave |
|
The first wave to arrive at seismic
station is P-wave. |
The second wave to arrive at seismic
station is P-wave. |
|
They are compression wave. |
They are shear waves. |
|
They can moves through solids and
liquids. |
They can only moves through solids. |